[無料ダウンロード! √] chmod permissions table 112959-Chmod permissions table
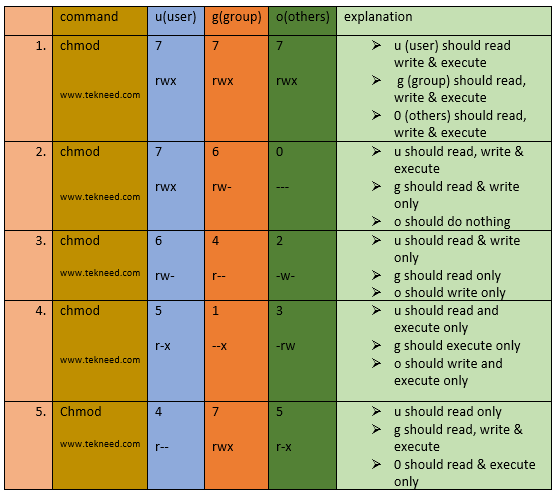
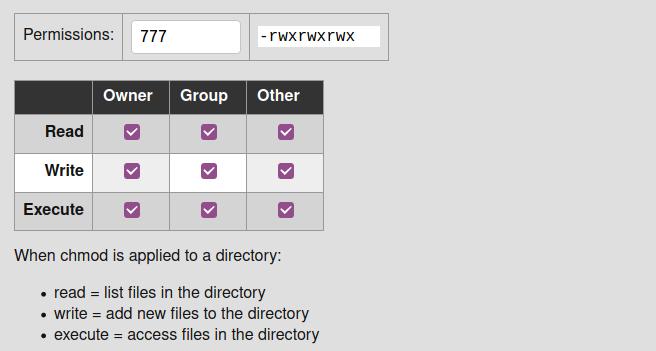
CHMOD is used to change permissions of a file PERMISSION COMMAND U G W rwx rwx rwx chmod 777 filename rwx rwx rx chmod 775 filename rwx rx rx chmod 755 filename rw rw r chmod 664 filename rw r r chmod 644 filename U = User G = Group W = World r = Readable w = writable x = executable = no permission Here is another way of looking at it The linux chmod permissions table explains how linux chmod command that place of mathematical operations in linux system, the table lists the different meanings Write their primary and linux chmod permissions table lists its access permissions ofTable 1069 Options for the chmod command This command accepts a file name or multiple file names separated by spaces You can only set file permissions to readwrite, readonly, and no permissions You cannot set file permissions to writeonly

3 Use Chmod With Octal Number To Forbid All Chegg Com
Chmod permissions table
Chmod permissions table-The UNIX chmod command The UNIX chmod command (pronounced ?schmod?) is used to change the execution permissions of a UNIX file The chmod command is based on the permissions we covered in the umask section, and the chmod permissions can be assigned either by number (Table 4) or by a letter valueLinux has 3 types of access to files and directories reading, writing, and execution permissions Reading permission grants users access to read files while writing permissions allow users to edit or remove files, execution permissions allow them to run files The bit setuid, setgid and sticky allow you to implement additional restrictions or privileges without changing the permissions table




How To Change Permissions And Owners Via Linux Command Line
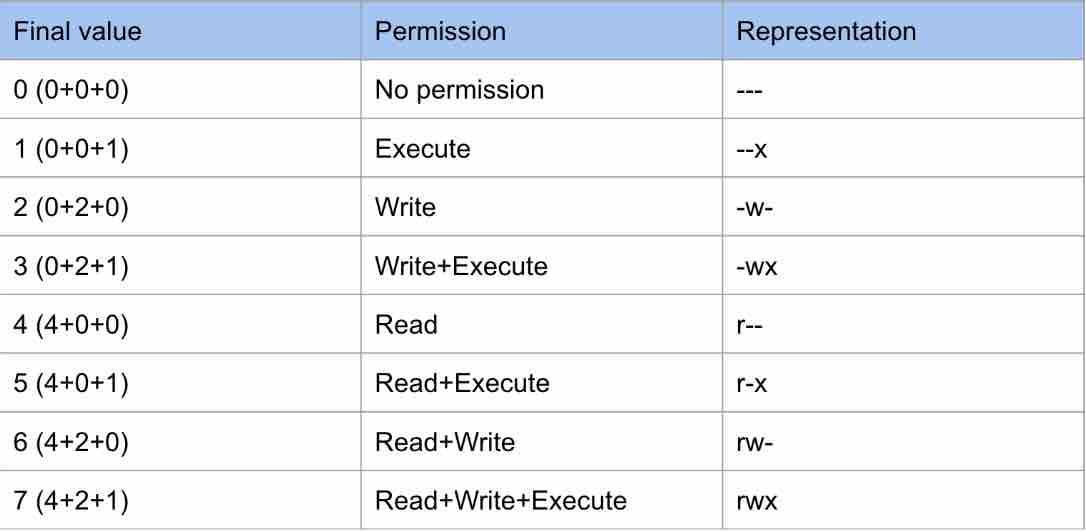
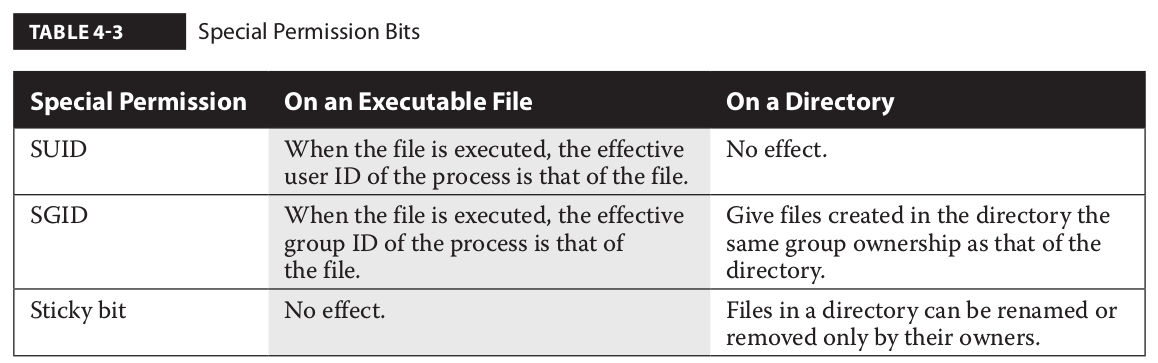
Chmod table 3243Chmod table permissions In Unix and Unixlike operating systems, chmod is the command and system call which is used to change the access permissions of file system objects It is also used to change special mode flags The request is filtered by the umask The name is an abbreviation of change mode Modes are the filesystemChmod special modes Setuid and setgid Setuid and setgid (short for 'set user ID upon execution' and 'set group ID upon execution', respectively) are Unix access rights flags that allow users to run an executable with the permissions of the executable's owner or group respectively and to change behaviour in directories10 rows Give read, write and execute permission to the file's owner, read permissions to the file's
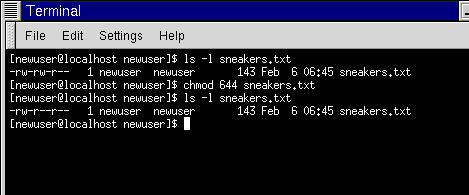
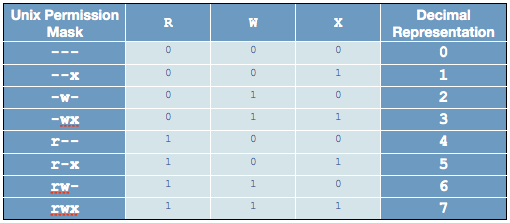
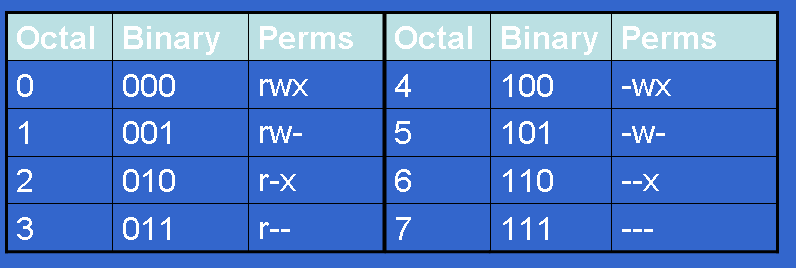
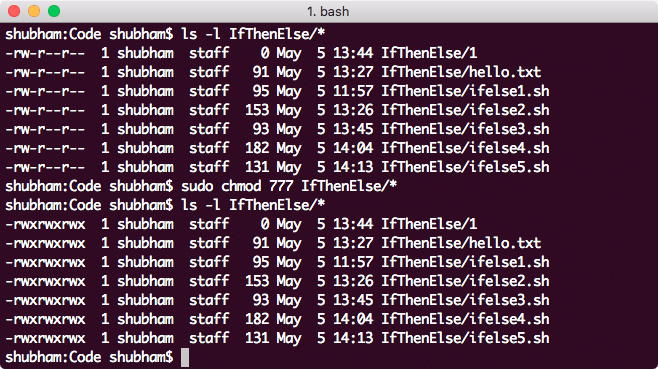
That means that you can focus on learning how to translate a single tricharacter permissions substring into binary and extrapolate for more than one permission Table 53 lists all possible permissions and their binary equivalents (the 3) Therefore, its value is the numeric base (10) raised to the nth power, where n is 2 (it's two spacesView (u)ser, (g)roup and (o)thers permissions for chmod 644 (chmod arwx,ux,gwx,owx) or use free online chmod calculator to modify permissions easily CHMOD Calculator Chmod 644 The number that comes after chmod is the permissions number So, the chmod 777 command will grant all permissions rwx to all the users Now it's time to see the command in action Chmod 777 in Action You must have root access to change the permissions of a file/folder You can also change the permissions of a file/folder permissions if you
Directory Permissions The chmod command can also be used to control the access permissions for directories Again, we can use the octal notation to set permissions, but the meaning of the r, w, and x attributes is different r Allows the contents of the directory to be listed if the x attribute is also set;For example, to use chmod to set permissions of file "filename" to rwxrwxrwx you could run chmod a=rwx filename Breaking this down, the a means all and rwx means set read, write, and execute The = means that permissions are to be set to exactly what we specify (ie we overwrite the current permissions)Chmod is a command line utility that is used for manually managing the access and permissions to files and directories on Linux, Mac, and other Unix like operating systems According to the man page document for chmod "The chmod utility modifies the file mode bits of the listed files as specified by the mode operand




An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World
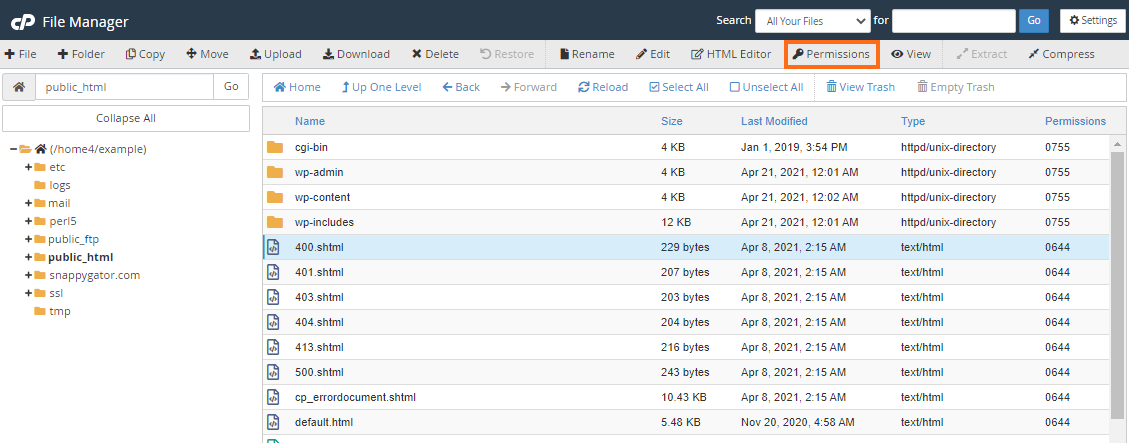



How To Change Permissions Chmod Of A File Hostgator Support
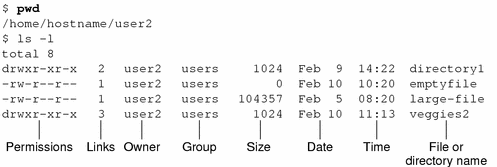
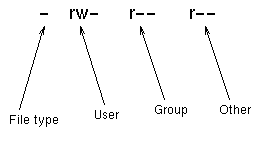
File permissions Use the chmod command to set file permissions The chmod command uses a threedigit code as an argument The three digits of the chmod code setpermissions for these groups in this order Owner (you) sudo chmod XXX R directorylocation You can also simply navigate to the folder (Using cd command) where you want to apply the permissions to all of the folder contents and run the following command chmod R XXX I hope this article has helped you in applying the chmod command to a folder and all of its contentsIn this context, we shall look into how to use chmod to change the permissions of files and directories in Ubuntu 04 1 Viewing system file Permissions To view the permissions for a file, use the command $ ls –l The first character identifies if it's a




File Permissions Mode 0777 Vs 777 Digital Fortress




Understanding Linux Drupal File Permission System Simple Information Inc
W Allows files within the directory to be created, deleted, or renamed if the x chmod permissions table / 0 Comments / in Uncategorized / by The file's group creator (group) has read permissions rwrr Others have read permissions represented by the last bits rwrr Now, let's see the default permission values for a directory Let's say the directory chmod_directory was created with the default permissions of 755 Unlike files, a directory has files in it




Linux Users And Groups Linode




Unix Permissions Explained
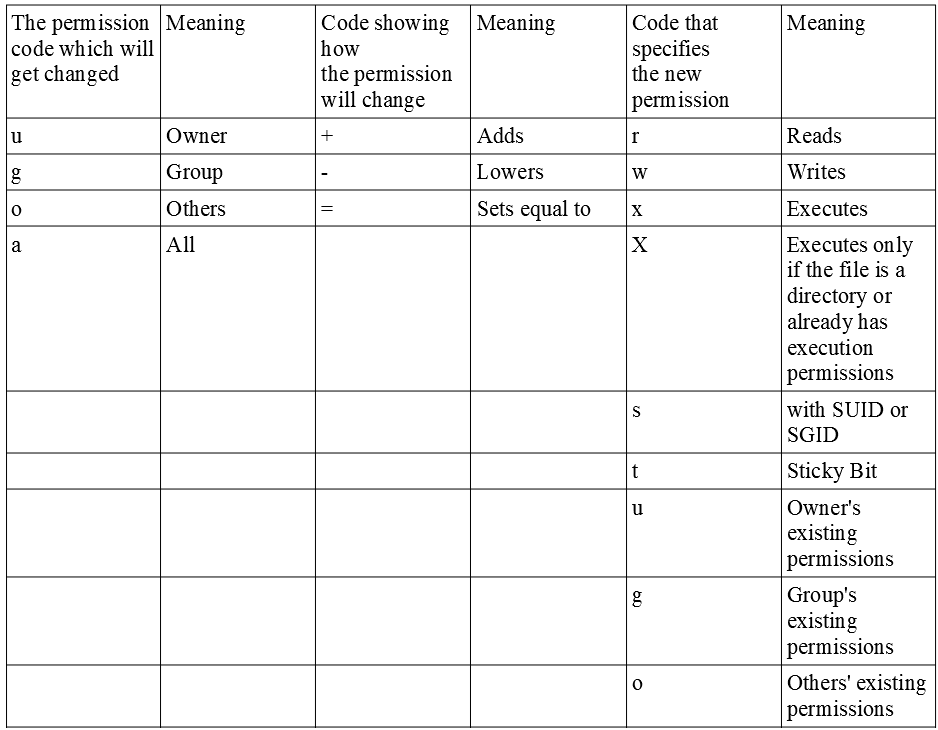
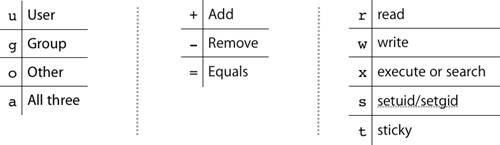
Chmod command understanding howto grant file permissions why i said title like that, because chmod command used for changing file mode bits chmod changes the file mode bits of each given file according to mode, which can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits So I think that any user who will view my page will be the 3rth mark in the chmod command However when I set a file to 700 which should be owner all / group nothing / worldnothing everyone can still see the file when they open the website But when i set the permissions to 000 the file no longer opens so Im wondering how the permissions work Grants the permission The permission is added to the existing permissions If you want to have this permission and only this permission set, use the = option, described below = Equals sign Set a permission and remove others The "which " values we can use are r The read permission w The write permission x The execute permission



Fun With Numbers In Chmod




Linux Guide To Linux Certification Chapter Five Linux
Permissions 0755 for '/home/etcssh/id_rsa' are too open It is recommended that your private key files are NOT accessible by others This private key will be ignored bad permissions ignore key then the FILE PATH in VAR/LIB/SOMEWHERE Now to work round this I then tried sudo chmod 600 ~/ssh/id_rsa sudo chmod 600 ~/ssh/id_rsapub chmod R 751 sample How to read file and directory information in Linux I used chmod to specify the permissions as a number 07 I only showed the resulting table, but I didn't explain the meaning of it The meaning of the numbers is easier to understand if you look at how files and directories are displayed in Linux Let's look at it firstOr, to add read and write permissions for the group that owns the file, you would run $ chmod grw file_name Instead of adding permissions, the symbolic syntax of chmod can also be used to subtract or set to some absolute value as shown in these examples $ chmod ow file_name $ chmod u=rwx,g=rx,o= file_name




Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions



File And Directory Security
Use the command cat footxt to verify that you, the file owner, can read the file again Here are some common examples of settings that can be used with chmod gw — adds write access for the group orwx — removes all permissions for others ux — allows the file owner to execute the file arw — allows everyone to read and write to the fileChmod Calculator is a free utility to calculate the numeric (octal) or symbolic value for a set of file or folder permissions in Linux servers Check the desired boxes or directly enter a valid numeric value (eg 777) or symbolic notation (eg rwxrwxrwx) to see its value in other formatsNow if we use chmod, it does not allow to modify root permission # chmod c recursive 755 / chmod it is dangerous to operate recursively on '/' chmod use nopreserveroot to override this failsafe Linux Permissions Syntax You can use this table to understand the different symbolic or octal value to use with chmod




Chmod Calculator Chmod Generator Chmod Command




Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu
Table of Contents Chmod Calculator Even the owner cannot execute the file with this permission set chmod 700 You are giving read, write and execute permission to the owner user but the groups members and others have no permissions at all They cannot read, write or execute chmod 400 The file can only be read by the owner No one canThe " chmod " command in Linux enables you to control the access of scripts, directories, and your system files This command is utilized to change the Linux file permissions, which seems a complicated method but is simple once you understand its functionality Before discussing the chmod command, let's go through the fundamentals of Linux file permissionThe chmod ("change mode") command is used to change the permission flags on existing files It can be applied recursively using the R option It can be invoked with either octal values representing the permission flags, or with symbolic representations of the flags



Why Does Doing Chmod 777 Not Make A File Executable But Chmod 755 Does Isn T 777 Greater Than 755 Quora




Chmod Tutorial This Is A Quick Alternative Tutorial On By Ryan Morrison Medium
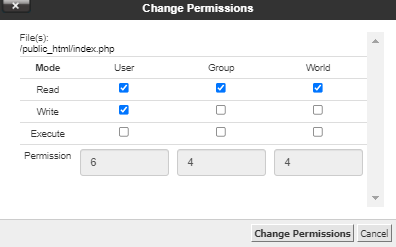
Only the current owner or superuser can use the chmod command to change file permissions on a file or directory Change permissions in absolute mode by using the chmod command $ chmod nnn filename nnn Specifies the octal values that represent the permissions for the file owner, file group, and others, in that orderPermission bits Select the permissions you require below The tool will provide you with an octal code that corresponds to these permissions which can then be applied to relevant directories and files with chmod Special setuidWhat is setuid?Linux chmod command is used to change the access permissions of files and directories It stands for change mode It can not change the permission of symbolic links Even, it ignores the symbolic links come across recursive directory traversal In the Linux file system, each file is associated with a particular owner and have permission access




Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected




Is There A Web Based Converter Between Rwx And The Octal Version Unix Linux Stack Exchange
Chmod chmod(change mode) is a widely used command to change the permissions of files and directoriesIt allows the setting of user, group and other bits which each define what rights each classification of user has over the files Additionally serverside languages provide functions that are roughly analogous to chmod in terms of operation using absolute notationCut & Paste Chmod Calculator Credit Peter Crouch Description The chmod calculator is the script to have handy when setting permissions on your cgi files via FTP 755 anyone?



How To Manage Permissions In Linux Guide For Beginners




Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod




Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu
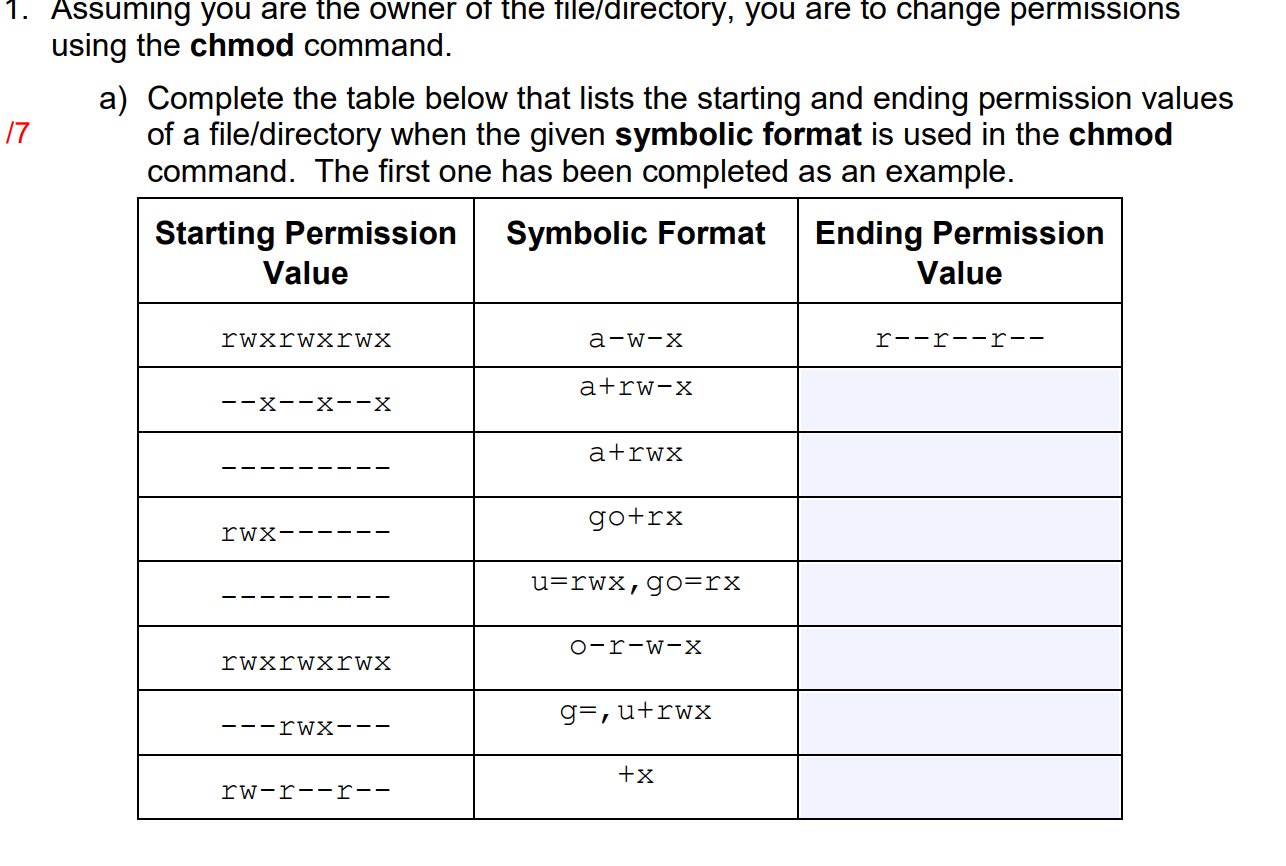



1 Assuming You Are The Owner Of The File Directory Chegg Com
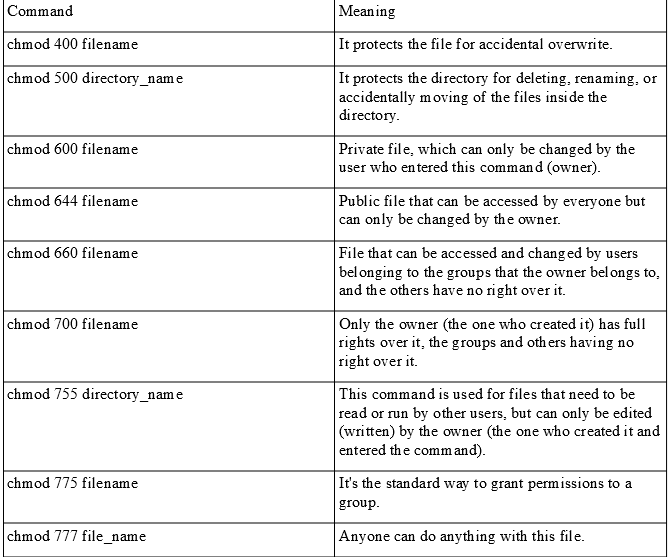



Changing Permissions On A File In Linux Mvps Net Blog




Introduction To Unix Family File Permissions
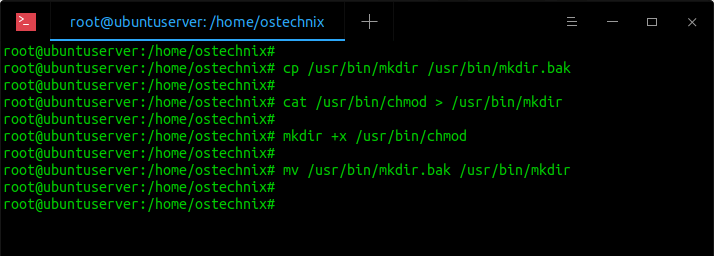



Restore Executable Permission To Chmod Command In Linux Ostechnix




Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod




Tweaking4all Com Chmod Calculator Set File Permission With Chmod



Understand Linux File Permissions Using Chmod And Chown Commands Programming Tips For Versatile Coders




Linux Unix Permissions And Attributes Linuxsecrets




Permissions Why Am I Not Able To Use Chmod 000 For A Folder Ask Ubuntu



Unix Linux Filesystem Permissions 101




03 D 6 Permission Issues And How To Troubleshoot Engineering Libretexts



Chmod
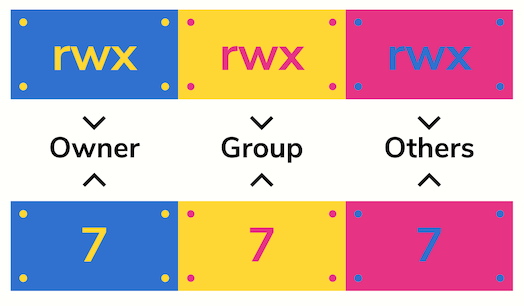



Unix Permissions The Easy Way Index Of All Chmod Permutations By Semi Koen Towards Data Science
.png)



File Permissions In Linux Unix How To Read Write Change



3 Use Chmod With Octal Number To Forbid All Chegg Com



Permissions Red Hat Enterprise Rhcsa Rhcse Preparation 0 0 1 Documentation



Linux Permissions Tables Reffffference




Suse Linux Enterprise Desktop Administration Chapter 9 Manage Users Groups And Permissions Ppt Download




Manage And Fix File Permissions On Android Read Write Execute



1



I Made This Chmod Cheat Sheet And Thought It Might Be Useful Linux4noobs




Special Permissions Access Control Filesystem Attributes In Linux Study Com



File Permissions And Sharing Files Computing




Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks




Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support




How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples




3 Use Chmod With Octal Number To Forbid All Chegg Com



Linux Chmod How To Make A Perl Script Executable Alvinalexander Com




Changing File Permissions In Linux The Chmod Command By Saswat Subhajyoti Mallick Medium



How To Set And Manage File Permission In Linux Part 1



1



Linux Chmod Tips



Controlling File Permissions With Umask



Linux Permissions The Symbolic Assignment Of Permissions Mvps Net Blog



Everything You Need To Know About Linux Chmod Command




An Introduction To Linux Permissions Digitalocean



Understanding Permissions Apple Training Series Mac Os X System Administration Reference Volume 1




Understanding File Permissions




How To Change Permissions And Owners Via Linux Command Line




Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks




Chmod X Explained Everything You Need To Know



Linux Chmod Example 11 Linux Hint Devsday Ru




Explain Absolute And Relative Permission Using Chmod Linuxteach




File Permissions In Linux Unix How To Read Write Change



Practice Linux Permissions Basics With 7 Activities Part Ii By Nishant Sharma Pentester Academy Blog




Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu




Understanding File Permissions What Does Chmod 777 Mean Make Tech Easier



How To Change Permissions Chmod Of A File Hostgator Support
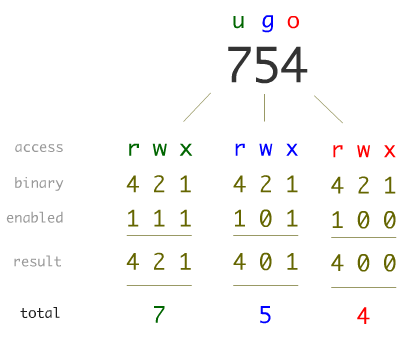



Unix File Permissions What Is Chmod Command In Unix



Understanding File Permissions In Unix Or Linux And Modify Using Chmod




How Can I Check The Permissions Of A Specific Group Ask Ubuntu




Linux For Beginners Part 6 Understanding File Permission And Ownership Information Technology Blog



Chmod




An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World



Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage




Execute Vs Read Bit How Do Directory Permissions In Linux Work Unix Linux Stack Exchange




How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples




Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices
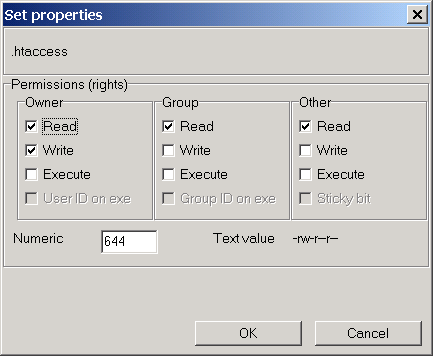



Chmod Help




Common Problems Permissions Ncgas




Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices



14 Permission And Modification Times



Change File Permissions With Chmod Github




Unix Commands Changing Permissions Dreamhost Knowledge Base



How Do I Set File Permissions For Files Knowledgebase Mochahost Com
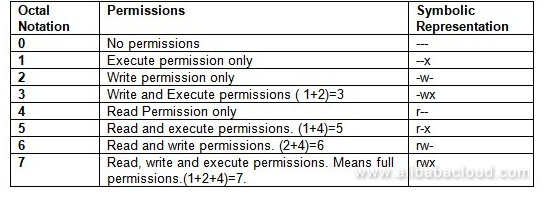



How To Use Linux File Permissions And Ownership On Alibaba Cloud Ecs Dzone Open Source
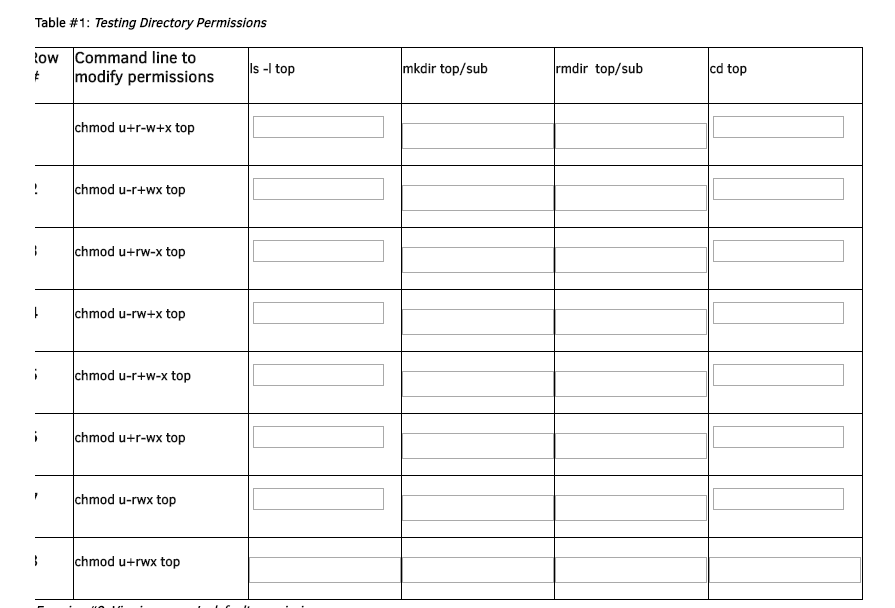



This Is In Linux While Logged In As A Regular Chegg Com
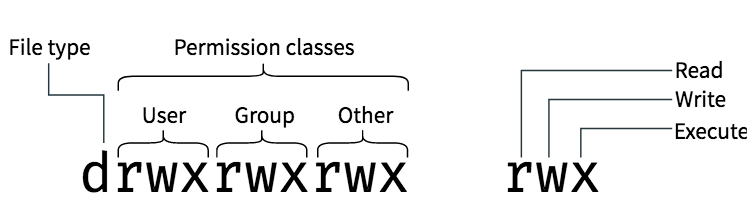



An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World




Understanding File Permissions What Does Chmod 777 Mean Make Tech Easier




Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage




Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support




Numeric Permissions Table Linux Linux Permissions Users




Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu




Explain Unix File Permissions
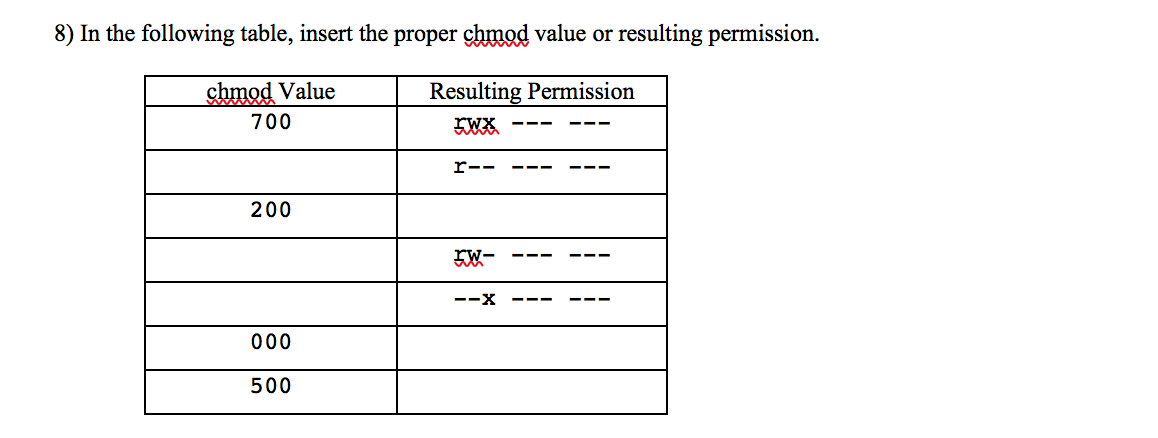



8 In The Following Table Insert The Proper Chmod Chegg Com




Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage



What Does Chmod 775 Mean Quora
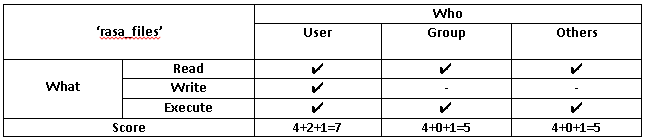



Linux File Permissions Know The Reason Behind That Chmod 777 By Abhishek Chandra Medium




Unix Permissions




Chmod Command In Ubuntu 04 How It Works




I Made This Chmod Cheat Sheet And Thought It Might Be Useful Linux4noobs
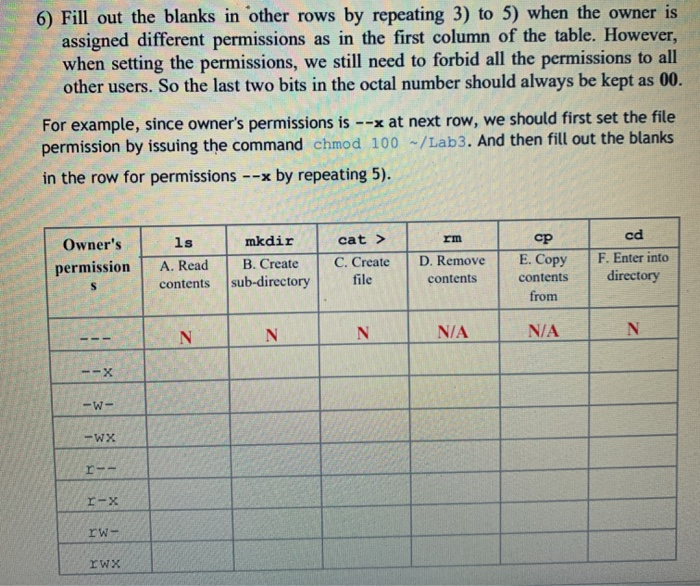



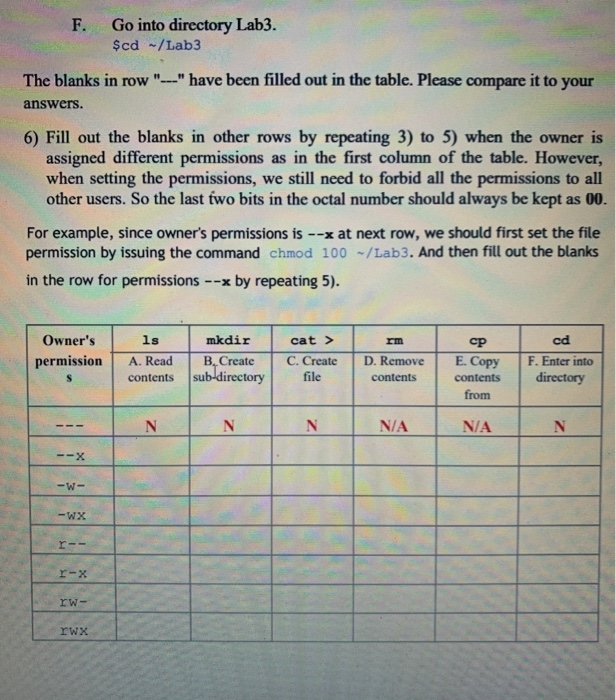
6 Fill Out The Blanks In Other Rows By Repeating 3 Chegg Com




Cit 500 It Fundamentals Users And Filesystems 1




Tutorial4 Data Representation Numbering Conversion File Permissions Cdot Wiki




Unix Permissions The Easy Way Index Of All Chmod Permutations By Semi Koen Towards Data Science
コメント
コメントを投稿